When it comes to cavities, you may have heard your child’s dentist talking about sealing or filling cavities. Since both of these sound like they could be the same thing, you are probably wondering just how they differ from one another. Chances are, you are also probably wondering which method is best for your child. To help you differentiate between the two methods, we’ve compiled this brief guide on sealing vs. filling cavities.
Sealing
When your child’s dentist talks about sealing cavities, they are talking about using something known as a dental sealant. Dental sealants are ultra-thin layers of composite resin that are placed over the chewing surface of molars and premolars. Like their name suggests, dental sealants effectively “seal” the tooth in order to prevent it from being compromised by decay-causing bacteria.
To apply a dental sealant, your child’s dentist will need to first clean your child’s teeth in order to remove any excess plaque, tartar, and bacteria from the surface. Then, the sealant can be brushed on and hardened in place with a special curing light. Since dental sealants are so easy to place, they generally only take a few minutes and do not usually require dental sedation or anesthetics.
Filling
On the other hand, dental fillings are used to fill in an area of damaged or decayed enamel. Most dental fillings are also made out of composite resin, since this material adheres to enamel, has a natural appearance, and minimizes the risk of allergic reactions. Dental fillings can be placed on any tooth in order to restore the affected tooth.
To apply a composite filling, your child’s dentist will need to prepare the affected tooth. Because composite resin can bond with enamel, there is not much preparation that needs to be done and the majority of your child’s natural tooth structure will be preserved. Next, your child’s dentist will fill the cavity by layering and hardening composite resin one layer at a time. It usually takes around three layers to fit a cavity, with the final layer being shaped and polished to blend with the surrounding tooth structure.
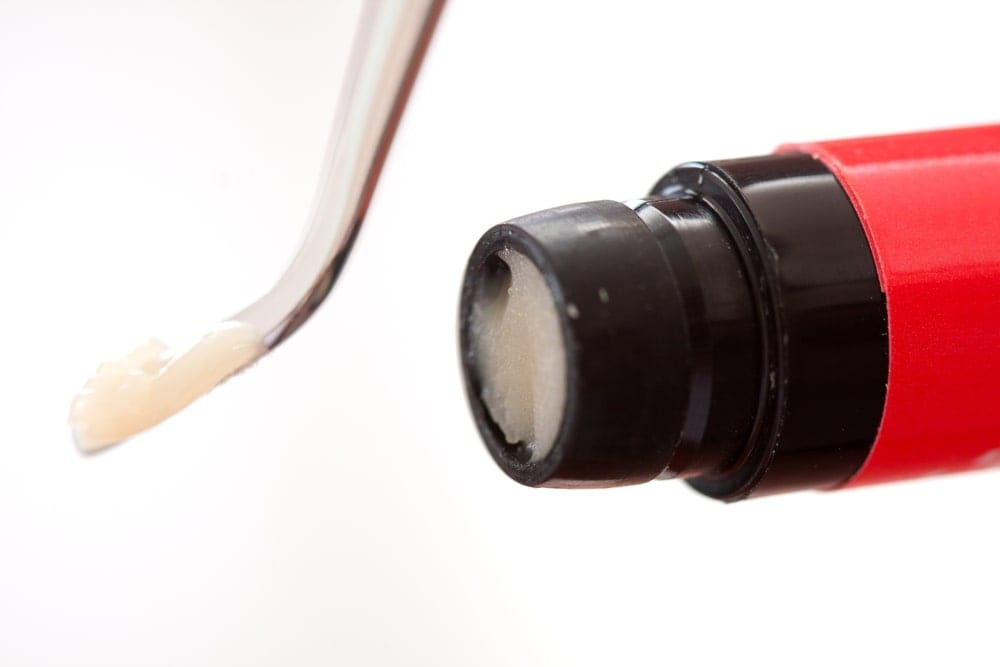

As you can see, both dental sealants and composite fillings use composite resin, however they use it in different ways. Dental sealants use an ultra thin layer of composite resin in order to seal out decay-causing bacteria and prevent the formation of cavities. In some cases, a tooth showing early signs of decay may be able to be treated using dental sealants.
As a general rule, however, teeth that have already been affected by decay will need to be restored using composite fillings. Unlike dental sealants, composite fillings apply multiple layers of composite resin in order to fill an existing small to medium cavity. Therefore the main purpose of a composite filling is restoration as opposed to prevention.
However, since both dental sealants and composite fillings are derived from composite resin, caring for your child’s teeth is the same whether they have had dental sealants or composite fillings placed. This means that your child will need to continue to brush twice a day with a fluoridated toothpaste and floss once a day. You will also need to continue to schedule regular dental exams and cleanings approximately once every six months.